How to Create a Budget for College

Creating a budget is one of the best ways to start managing your money wisely. Follow these tips – and use our free budget template – to get started.
Adapted from 1st Financial Bank USA's Blog
College brings a wide variety of new activities and an exciting sense of freedom, but this new freedom can negatively effect your finances if you aren't careful. If you're a student who is beginning to prioritize your future and plan to achieve larger financial goals down the road, the practice of budgeting is essential. Budgets can act as an invisible conscience reminding you that you don’t need to order your third pair of shoes this month, even if there was an “amazing sale.” Plus, following a budget in college may create a financially sound habit that can benefit you throughout your life.
Before getting started, download and print our free monthly budget template. While that is printing, read further to learn about different kinds of expenses, how they can impact your budget, and the steps you'll need to follow to create a proper budget for college.
What are the types of expenses?
Personal expenses can be separated into two different categories, fixed and variable expenses. It’s important to identify the differences between these expenses when creating your monthly budget in college.
Fixed Expenses
A fixed expense is a recurring cost paid regularly (weekly, monthly, quarterly, or yearly). The amount you pay for a fixed expense doesn't usually change or changes very little. Some examples of common fixed expenses are a college meal plan, rent, insurance, subscriptions, and car payments. The amount that you pay towards student loan debt or debt from credit cards on a monthly basis could also be considered a fixed expense.
Most fixed expenses are essential, but there are a few costs that are fixed and non-essential. For example, a streaming service may cost $10 per month. Although this cost is fixed from month to month, you don’t necessarily need a streaming service to survive. Therefore, you would consider a streaming service a fixed non-essential expense.
Utilizing student discounts is a good way to help you reduce the cost of some of your non-essential monthly expenses. Some of these “non-essential purchases” could be considered essential in moderation and in certain circumstances.
Variable Expenses
A variable expense is a potential cost that varies each month depending on your personal spending decisions. Variable expenses include gasoline, car maintenance, groceries, phone bills, and so on. For example, if you have a phone plan that charges you based on the number of calls you make, a month that you make 20 calls will cost less than a month that you make 35 calls. The same concept occurs with gas expenses. If you don’t drive your car, you won’t have to fill up with gas as often. Essentially, variable expenses change with your usage of the item.
All of the expenses listed above are essential variable expenses. Non-essential variable expenses are purchases that might be fun to make, but that you don't necessarily need to make. Concerts, eating out, movie tickets, gifts, and vacations are all forms of non-essential variable expenses. They are fun, the prices of these items vary and they are not considered an essential need.
Non-essential variable expenses are often where the most money is wasted in a budget. It is up to you to decide when to spend your money on non-essential items and when to save that money for an item in the future.
Creating Your Budget
Now that you’ve learned about the different kinds of expenses, you’re ready to get started on creating your budget. Before we begin, make sure that you have your budget sheet, a calculator, an extra piece of paper, and a pencil ready. You will be following along through the steps while customizing the budget sheet to your own lifestyle.
Step 1: Determine Average Monthly Income
Your average monthly income will give you an estimate to determine the amount of money you have available to spend on essential and non-essential purchases this month. To calculate your average monthly income, you will add all of your income over the last three months to get a three-month total. Then you will divide by three to come up with the average. Be sure to include any part-time job and regular pay into your income; it’s important to keep track of everything!
Step 2: Recognize Fixed Expenses
Now that you have recorded your monthly income it is time to look over your fixed expenses. Double-check that the fixed expenses that were listed above apply to you. If those expenses don’t, you can cross them off. Feel free to add any expenses we missed in the “other:” rows as well.
As a college student, it is important to think of the future, especially financially. A fixed expense can also be money put aside for a savings account. If you’re a college student who is paying off student loans or incurring costs for tuition and fees, consider adding “monthly savings” as a fixed expense to kick-start your savings.

Step 3: Calculate Fixed Expenses Amount
The next step is to calculate and write down the cost of your fixed expenses. Remember, fixed expenses are costs that stay the same, so little to no calculation should be needed. In the boxes provided under the “Amount” column, write in the monthly cost of your fixed expenses.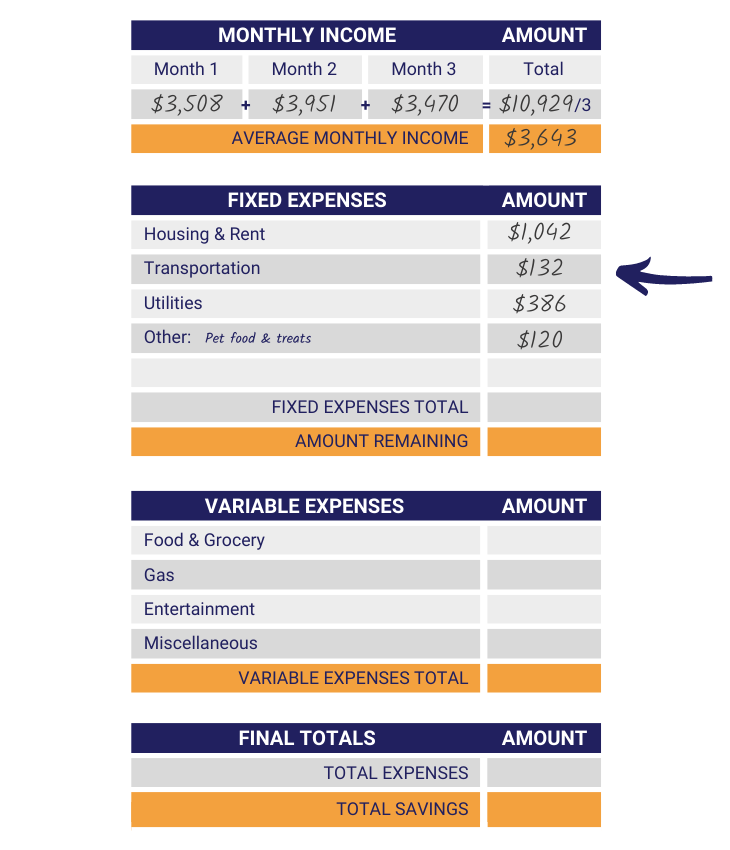
Step 4: Total Fixed Expenses Cost
The fourth step in creating your budget is to add the cost of your fixed expenses together and write in the gold box next to “Fixed Expenses Total.” Be sure to double-check your work and make sure you’ve added it correctly!

Step 5: Figure Amount Remaining
The next step is to calculate the amount remaining after Fixed Expenses. This is important because it separates the purchases you must make from the purchases you choose to make. To find the amount remaining, you subtract your Fixed Expenses Total from your Average Monthly Income. Write the answer on the Amount Remaining row.
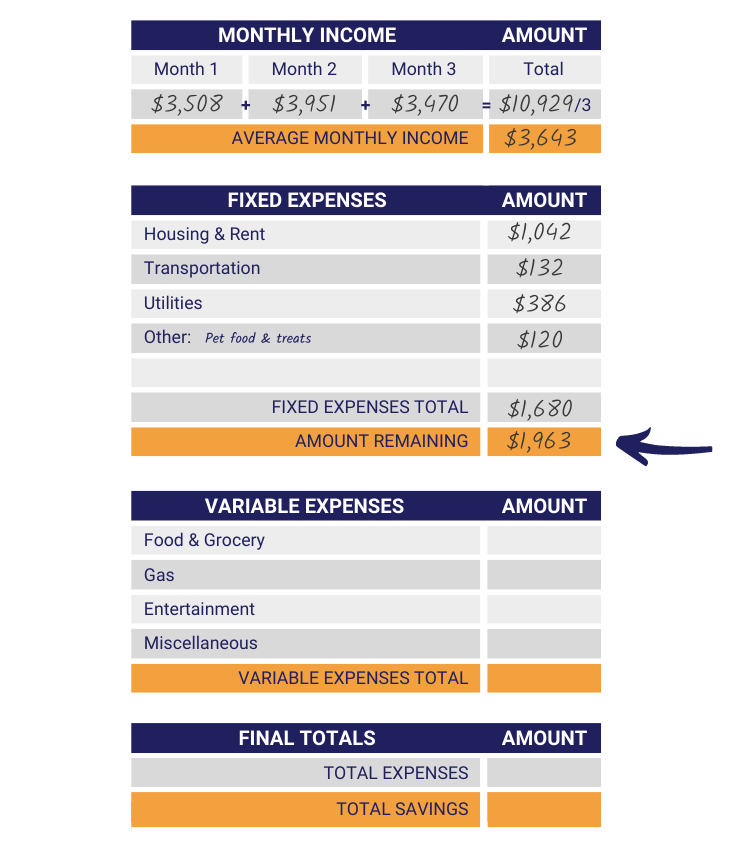
Step 6: Recognize Variable Expenses
Now it’s time for variable expenses. Using a separate sheet of paper, make a list of your variable expenses and estimate how much you would spend on them monthly. Try to keep the list as short as possible by condensing some expenses into a broader topic.
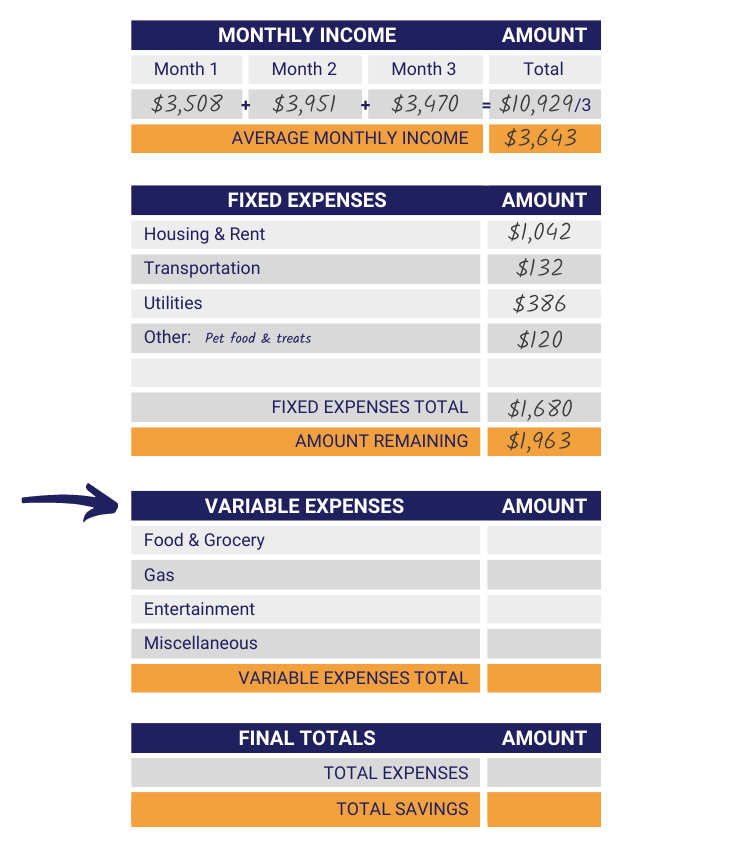
Step 7: Estimate Variable Expenses Cost
For step seven, estimate the monthly cost of each variable expense and write the prices in the “Cost” column. If you have variable expenses that are not labeled on the sheet you can include their price in the “Miscellaneous” cost row.
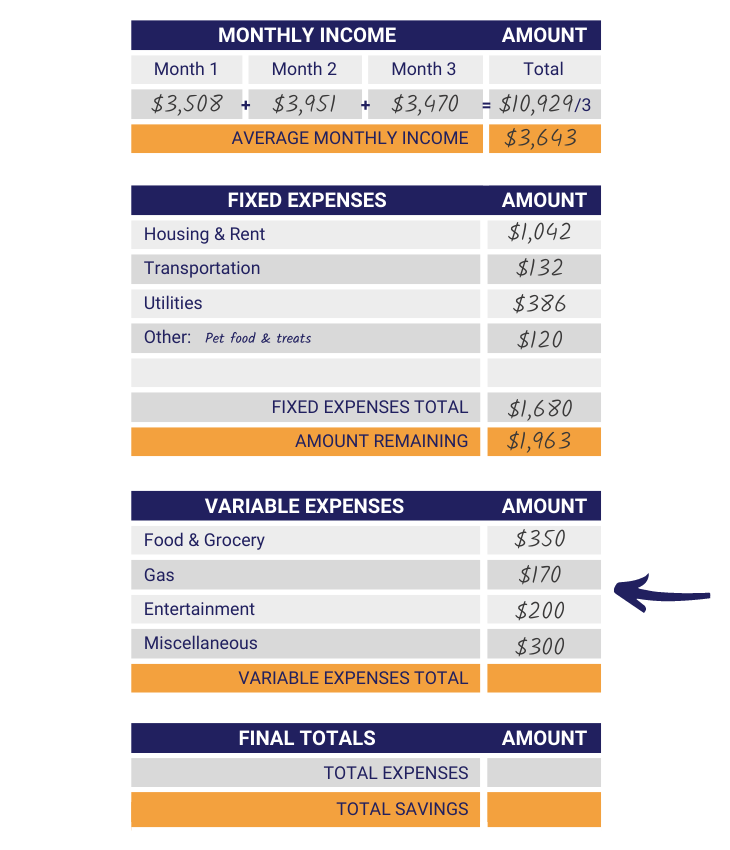
Step 8: Total Variable Expenses Cost
The next step is to add together the costs of your Variable Expenses. Once you have done that, write your answer in the space provided next to “Variable Expenses Total.”
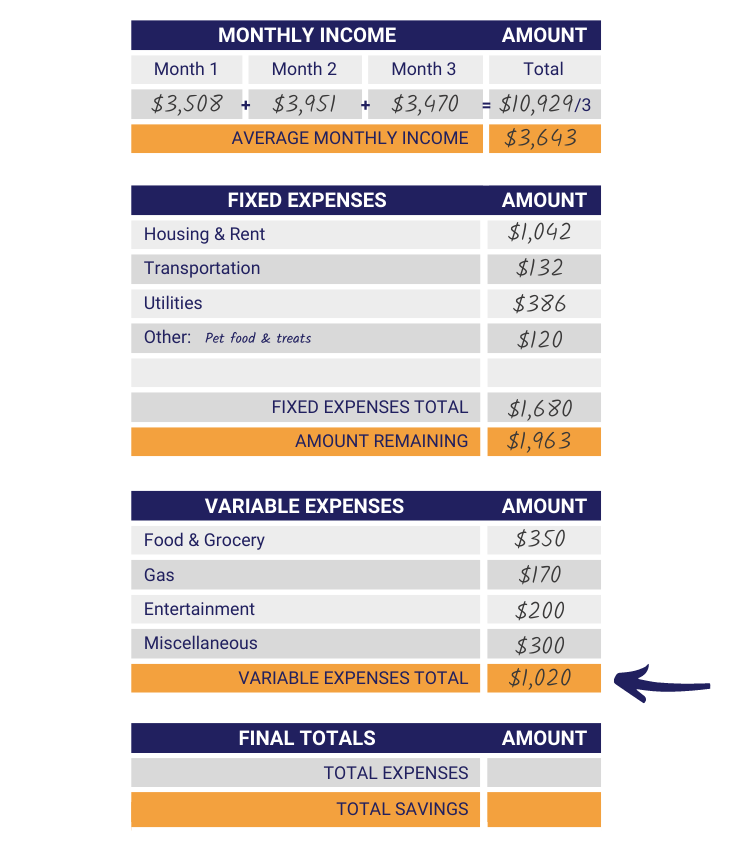
Step 9: Calculate Total Expenses
Now that you have successfully calculated both your fixed and variable expenses, your next step is to find the sum. To do this, add together the “Fixed Expenses Total” and “Variable Expenses Total” amounts and write your answer in the provided space next to “Total Expenses.”

Step 10: Find Total Savings
The final step in building your budget is to find your total savings. To do this, subtract the final total expenses from your Average Monthly Income. Once you’ve done that, record your answer in the gold box next to “Total Savings.”
Although it is up to you what you do with your total savings, we recommend putting the remaining money into your savings account or an emergency fund. You never know what the school year might hold, and it never hurts to have some money saved up in case any unexpected college expenses come up.

Congratulations! You have successfully followed along and completed your personal monthly budget. Filling out and following a budget sheet every month will help keep your bank accounts and finances in check. It is important to budget your finances, even if you don’t use paper. An alternative would be to try a budgeting app to keep you on track.
We hope that this step-by-step guide helps you track your spending, build your college student budget, and save you money. Create a budget today; your future self will thank you!





